In the heat of the summer, it’s common for individuals to seek out the beach or their backyard pool to soak up as much sun as possible.
But did you know that you can get a sunburn during your first 15 minutes of exposure to the sun’s harmful UV radiation? Even worse, sun poisoning can occur if you expose your skin for longer than that.
Sun poisoning is a severe kind of sunburn brought on by excessive time spent in the sun and can prove extremely painful. It can also lead to melanoma, a horrible form of skin cancer.
Table of Contents
What is sun poisoning and how does it happen?
Sun poisoning, despite its name, is not a poison in the traditional sense. There are a few different ways to define “sun poisoning.” The most common use of the term is to describe a particularly bad case of sunburn.
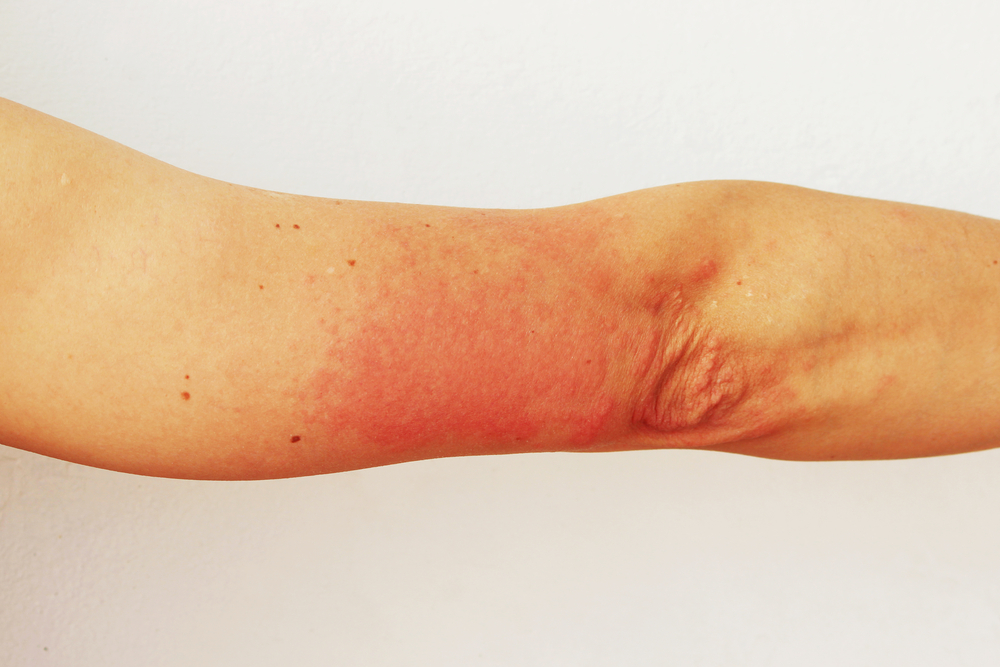
Another example could be photodermatitis, which is the technical term for any aberrant reaction to sunlight. When it comes to sunburn and sun poisoning, many people are confused.
Sunburn-like symptoms are present in all kinds of photodermatitis, but some can induce extra rash-like symptoms.
Can sun poisoning affect your DNA?
Damage to DNA and cell death can be caused by the sun’s damaging UV radiation. In most cases, your body’s reaction to a burn takes several hours.
As a result, you may not become aware that you’ve been sunburned until much later that night.
You may be unsure of how to appropriately recognize sun poisoning cases. Besides a sunburn, the following are common signs of sun poisoning:
- Noticeable blisters: Depending on the severity of the blistering, it can range from a little, barely noticeable blister to a huge, water-filled, red, sensitive, and raw skin blister. When a blister ruptures, the surrounding skin will peel away.
- Fevers
- Headache
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Dehydration
- Swelling
- Peeling skin or skin loss approximately 4 days to a week after exposure to excess sun.
How do you treat sun poisoning?
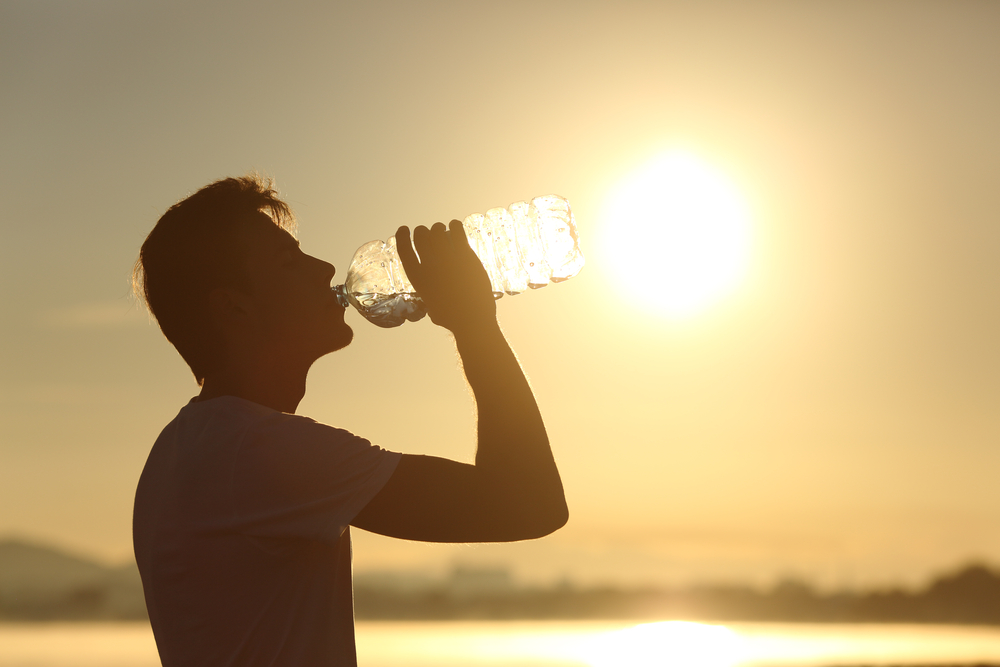

In hopes of preventing additional injury, sun poisoning must be treated differently than a conventional sunburn. You can treat sun poisoning in several simple ways.
The first move is to get out of the sun and seek some shade, then:
- Take a cool (not icy) shower or dampen your clothes to keep your skin at a comfortable temperature.
- Consume enough liquids to keep your body well-hydrated during the day.
- Take aspirin or other pain medicines if necessary to alleviate your suffering.
- You can apply Aloe vera gel to the section of your skin that has been burned.
- If you are unable to stay inside, cover up any areas that received damage.
If you see that your symptoms of sun poisoning are getting worse, you should visit a doctor immediately.
What you need to know about preventing sun poisoning
Sun poisoning is often excruciating, but it can also be easily avoided. You can keep having great fun as long as you take the proper measures.
To avoid sun poisoning, follow these simple guidelines:
Avoid the midday sun. Between 11 a.m. and 2 p.m., the sun’s rays are at their strongest.
If you can, plan your outdoor activities for the early or late hours of the day.
When going outside, apply a large dose of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin. Also, reapply it every two hours to avoid it being washed away by perspiration.
While it’s normal that you’d like to spend as much time outside as possible to take advantage of the nice weather, you should take precautions to limit your exposure to the sun. However, if you are prone to sunburn, you might benefit from an indoor day.
Protect yourself from the harmful effects of too much exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays.
What percentage of Americans get sun poisoning?
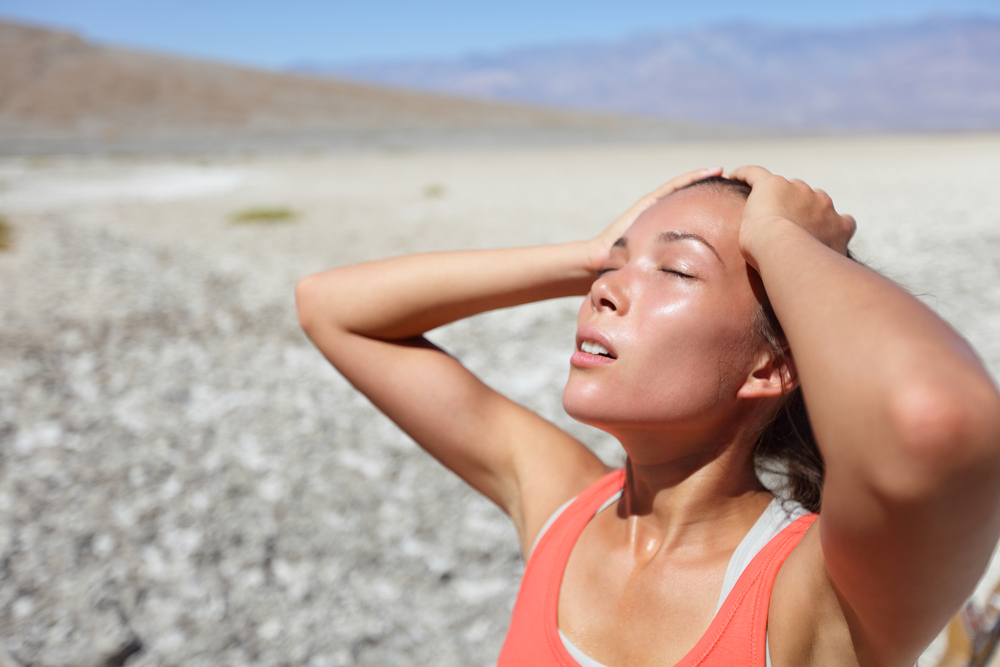

Due to a condition known as polymorphous light eruptions, some people get sunburned (also referred to as sun poisoning or PMLE). PMLE is a reaction that affects about 10% of the population and does not seem to be caused by drugs or illnesses.
In only half an hour to a few hours of exposure, the moderate to severe skin redness known as PMLE begins to appear.
The following symptoms may accompany the rash:
- Itching all over the body, but especially in areas that are exposed to the sun
- Bumpy clusters of redness are the final stage of sun rash
- Hives, most commonly on the arms, legs, and chest
How severe can sun poisoning get?
A severe case of sunburn or sun poisoning is rarely deadly, but it can be extremely painful and disabling. According to a Skin Cancer Foundation poll, only one in three respondents claimed getting scorched at some point in the last year.
As per the Skin Cancer Foundation, a person’s risk of acquiring melanoma later in life is more than doubled if they get one or more severe sunburns as a kid or teenager.
If a person has had five or more sunburns in their lifetime, their risk of developing melanoma doubles. Shock (insufficient blood flow to major organs) and even death can result from severe unmanaged sunburn.
What is melanoma?
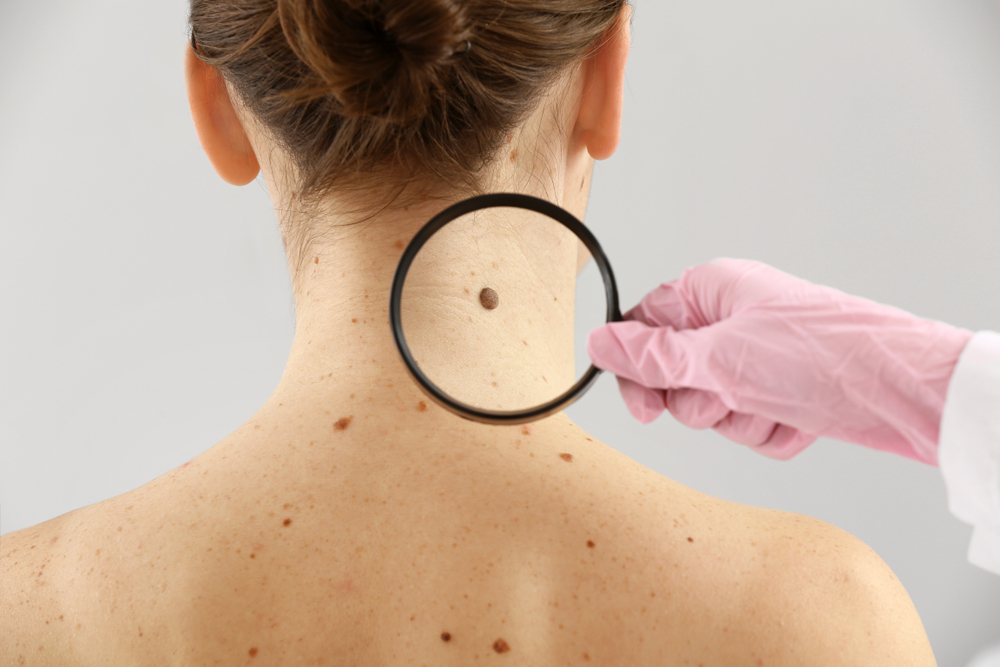
Melanoma, the most severe form of skin cancer, advances in the organisms (melanocytes) that produce melanin (the substance that gives one’s skin its color). Melanoma can also develop in the eyes, nose, or throat, but this is extremely unusual.
Sunlight or tanning lights and beds can raise your risk of acquiring melanoma, although the concrete evidence of all melanomas is not known. Minimize your chances of melanoma by restricting your exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet radiation.
Melanoma is becoming more common among adults under the age of 40, particularly among women. It is important to be able to identify the signs of melanoma to prevent it from spreading.
If identified early enough, melanoma can be successfully treated.
What are the signs and symptoms of melanoma?
Melanomas can appear anywhere on the body. Your back, thighs, forearms, and face are some of the most common places to see them form.
The bottom of your feet, the middle of your hands, and the fingernail beds can all develop melanoma even if they don’t get a lot of direct sun exposure. People with darker skin are more likely to have these hidden melanomas.
The following are common early indications and symptoms of melanoma:
- The emergence of a new type of mole
- The appearance of a fresh, pigmented, or otherwise odd-looking skin growth
- Melanoma doesn’t have to begin as a mole to become cancer. It can also appear on skin that appears normal
What are normal moles?
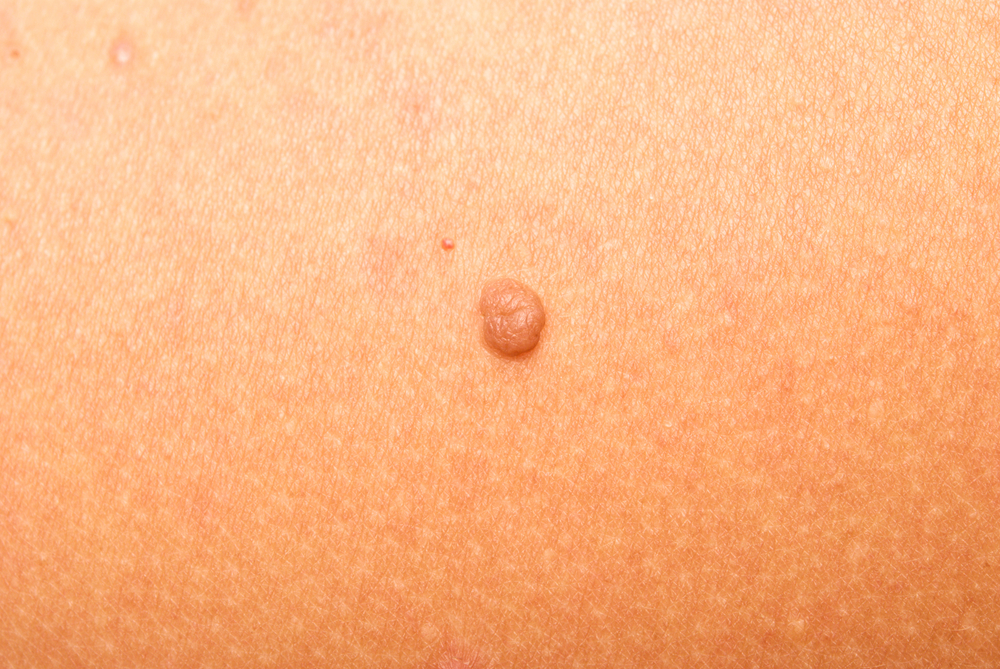
Moles that don’t cause concern are known as “normal moles.” In most cases, moles have a clear border and are a consistent hue, such as tan, brown, or black.
The majority of moles emerge in childhood, and new moles can appear up to the age of 40. Most individuals have around 10 to 40 moles by the time they reach adulthood.
Moles can change in appearance or even disappear with time.
What are abnormal moles?
Melanoma-initiating moles that are out of the ordinary. Consider the characters ABCDE to help you recognize characteristics of atypical moles that could signify melanomas or other forms of skin cancer:
1. A is stands for abnormal. Look for moles that have an odd shape, such as two sections that are completely dissimilar in appearance.
2. B stands for “irregular borders.” It’s important to look for moles that have asymmetrical or scalloped edges, which are hallmarks of melanomas.
3. The letter C stands for change in color. Colorful or unevenly distributed cancerous growths need to be checked out.
4. D stands for diameter. A mole that is more than one-fourth of an inch in diameter may be showing signs of fresh growth (about 6 millimeters).
Be on the lookout for changes all the time, including an expanding or changing mole. New signs and symptoms, such as itching or bleeding, may arise as moles mature.
There is a wide range in the appearance of cancerous (malignant) moles. Every one of the changes stated above may be present in some individuals, while others may display only one or two of the above-listed characteristics.
How long can melanomas go unnoticed?
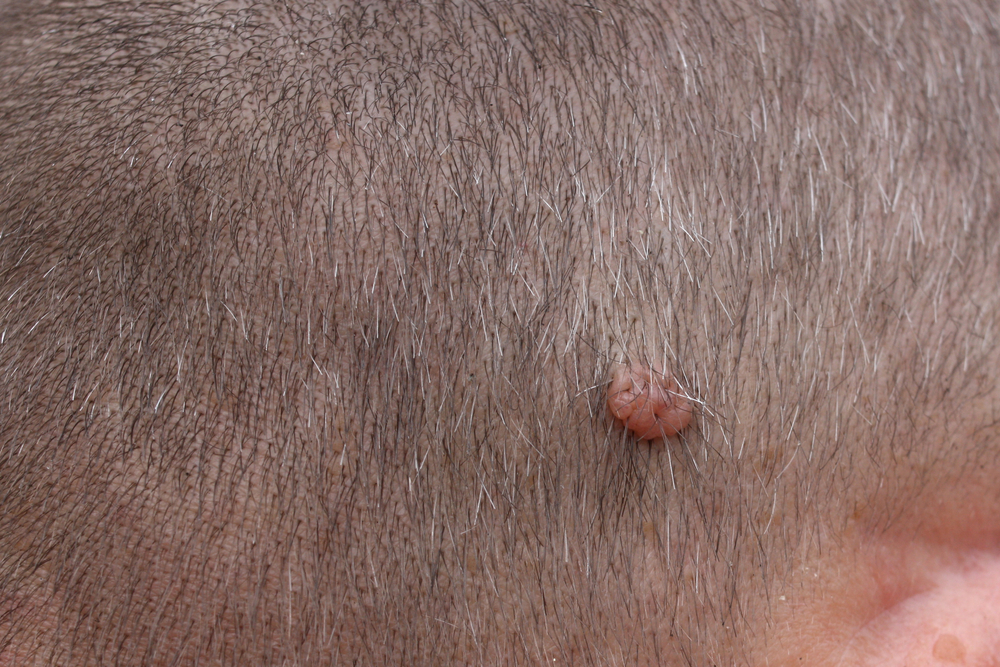
Melanomas can generate in regions of the body that are not exposed to the sun, such as the interdigital spaces between your toenails and the palms, soles, and scalp.
Hidden melanomas are called such because they are found in places where most people would never look. Individuals with darker skin are more prone to develop melanomas in an obscure location.
Is melanoma the result of sun poisoning?
It is still a mystery as to what causes the DNA damage in skin cells that leads to melanoma. Melanoma may be caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors.
The principal reason for melanoma, practitioners believe, is UV radiation from the sun, tanning lamps, and beds.
All melanomas, notably those that arise in areas of the body that are not exposed to sunlight are not caused by UV rays. These findings suggest that you may be at a greater risk of developing melanoma due to additional risk factors.
What are the risk factors for melanoma?
The risk factors of melanoma can be increased by several factors, including:
Skin that is light in color: Melanin is a skin pigment that helps protect against the sun’s harmful rays. When it comes to melanoma, having blonde or red hair, blue or hazel eyes, and freckles or sunburns easily increases your risk.
Blacks and Latinos, as well as other people of darker skin tones, can develop melanoma.
Sunburns in the family tree: Melanoma is more likely to develop in people who have had multiple severe, blistering sunburns.
Overexposure to UV rays: There is some evidence that UV exposure from the sun, tanning lamps, or beds can raise the cancer risk, particularly melanoma.
Living at a higher altitude or closer to the equator: Higher levels of UV radiation are experienced by those who live near the Earth’s equator than those who live further north or south.
The more elevation you have, the more UV rays you’ll be exposed to.
Moles that are unprecedented in number and appearance: Melanoma risk is enhanced if you have more than 50 moles on your body.
Melanoma is also more likely to occur if you have a mole that is atypical in shape or color. Dysplastic nevi are bigger than usual moles, with unusual borders and a variety of colors.
They are scientifically known as dysplastic nevi.
Melanoma runs in the family: Close relatives, such as parents, children, and siblings, have an increased risk of acquiring skin cancer themselves.
The immune system is weakened: Melanoma and other skin malignancies are more common in those with compromised immune systems. A weakened immune system can result from using an immunosuppressant medication, like after a transplant, or from having an immune system-depleting disease like HIV/AIDS.

















