Absolute monarchies are an arrangement of government where one person – usually a queen or king –holds the absolute, autocratic power.
In absolute monarchies, the power succession is usually hereditary, with the throne being passed to members of the ruling family.
Today, seven countries: Brunei, Eswatini, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Vatican City State, and the United Arab Emirates, remain absolute monarchies.
Table of Contents
Which countries still have an absolute monarchy?
Brunei
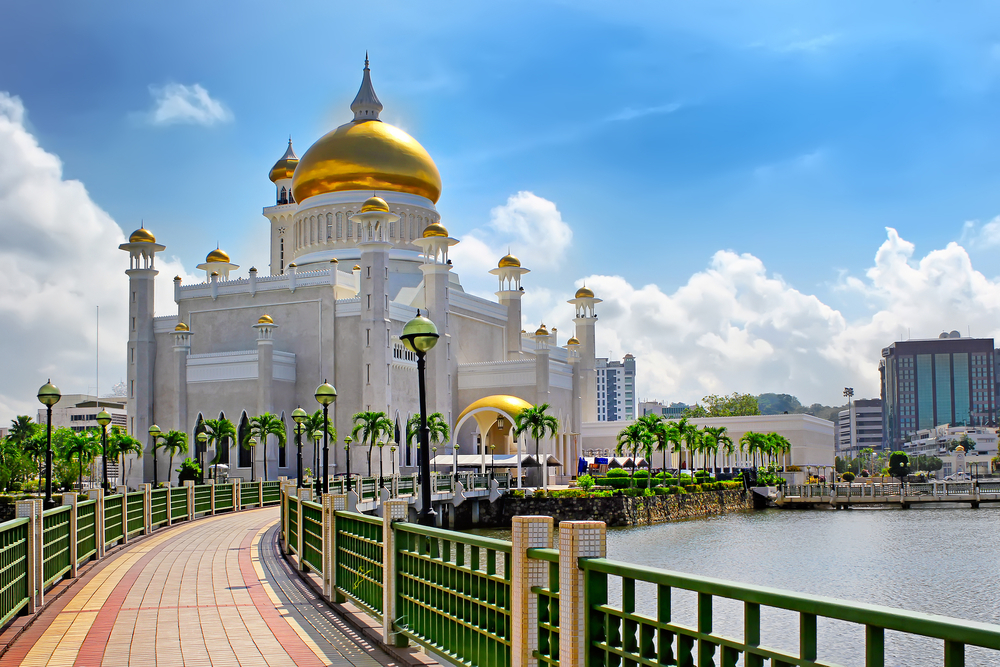

The Sultanate of Brunei and absolute monarchy
This country is on the island of Borneo in southeastern Asia and its capital city is Bandar Seri Begawan. (Bandar means ‘town’ in Malay, the official language of Brunei.)
The lifestyle of Brunei’s absolute monarch
A family of the same lineage has ruled Brunei for more than six centuries. In 2017, Brunei commemorated the 50th-anniversary celebration of King Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah’s ascendance to the throne.
The Sultan of Brunei is one of the world’s wealthiest men (estimated to have a net worth of around US $20 billion). It is also believed that he has been in a bit of a tumultuous relationship with various lovers.
The Sultan was married to his first cousin, princess Saleha. The second wife of the Sultan worked as a pilot at Royal Brunei Airlines.
The Sultan divorced his second spouse in 2003 and stripped her of her royal status. A year later, the Sultan married a TV host who was 33 years younger than him.
In 2010, the Sultan split with the show host and took away her monthly allowance. In 1997, the royal family employed the former Miss USA Shannon Marketic and other beauty contestants to perform and host celebrations.
The women later filed serious accusations against the Sultan.
At one time, the Sultan’s net worth was up to $40 billion. His activities included racing Ferraris in the dark of Brunei’s capital city, constructing a palace with 1,788 rooms, and spending $20,000 on a single haircut.
Background and a short history of the Sultanate of Brunei

The influence of Brunei’s Sultanate was at its peak between the 15th–17th century as it was able to control the coastal regions of northwestern Borneo and the southern Philippines.
Brunei then entered a time of decline caused by internal conflicts over succession to the royal family and the colonial expansion of European powers.
Brunei is blessed with vast natural gas and petroleum fields, which is the reason for it having one of the highest per-capita GDPs worldwide.
Eswatini

From Swaziland to Eswatini, a change of name controversy
Eswatini (known informally as the Kingdom of Eswatini) was previously known as Swaziland (as it is referred to in English).
The name change was made public by the nation’s king on April 19, 2019, the 50th birthday of the King.
The announcement came as a surprise. However, King Mswati III had been using this new name in his speeches for a long time, so it should not have come as a surprise to anyone.
Eswatini, or eSwatini?
How is this country’s name spelled? Unfortunately, there is plenty of confusion surrounding this.
Most authoritative sources spell the name the usual way, beginning with a capital letter.
However, there is plenty of evidence that the name should start with a small ‘e’ and a capital ‘S,’ like the name of a variable in computer code.
Eswatini and absolute monarchy
In Swati tradition, the king must marry women from different clans to maintain nationwide unity. King Mswati III is no different.
The King has fourteen wives, each of whom has at least one child. But determining how many offspring the king has had is a challenge.
In Eswatini, it is forbidden to divulge details about the king’s private life, including the number of children he has.
The future of the absolute monarchy in Eswatini

Who the future monarch will be is unknown because the rules for succession are ambiguous, and a monarch cannot choose his successor.
Instead, the heir to the throne is selected based on the status of his mother.
In the event of the King’s death, the Royal Council chooses the new Queen Mother by her status and her character. She can’t be one of the King’s “ritual wives” – the first two he married.
When the Queen Mother is chosen, her son becomes the future king and absolute monarch.
Eswatini background and short history
The autonomy of Eswatini was granted under the British in the latter 19th century. Independence was declared in the year 1968.
Classified as a lower-middle-income country, Eswatini suffers from severe poverty and high unemployment.
It is home to the world’s highest rate of HIV/AIDS, but recent years have witnessed notable declines in new cases.
Oman

Oman and absolute monarchy
Oman was ruled by the famous Sultan Qaboos for more than a century until his death in 2000.
Under the leadership of Sultan Qaboos, Oman transformed into a modern state from an Arabian Peninsula backwater.
Although the official media did not mention Dhi Yazan as the heir, a royal decree issued on January 12 stated that the crown would henceforth pass to the oldest son.
Therefore, the succession lines in Oman have become more established, and any uncertainties that could cause tensions are now less likely.
Many Omanis – particularly the younger generation – have been ecstatic about the selection of the heir and have congratulated him on social media platforms.
Oman background and short history
The Omanis living in the region of Oman have long enjoyed the benefits of the Indian Ocean trade.
In the 1800s, Oman’s newly formed Sultanate of Muscat made the very first of several friendship agreements with Britain.
As time passed, the dependence of Oman on the British military and political advisors intensified, even though the sultanate was never an official British colony.
Qaboos bin Said Al-Said took over from his father in 1970 and became the Sultan.
Sultan Qaboos does not have children and hasn’t named an official successor; however, the Basic Law of 1996 outlines the succession process in Oman.
Qatar
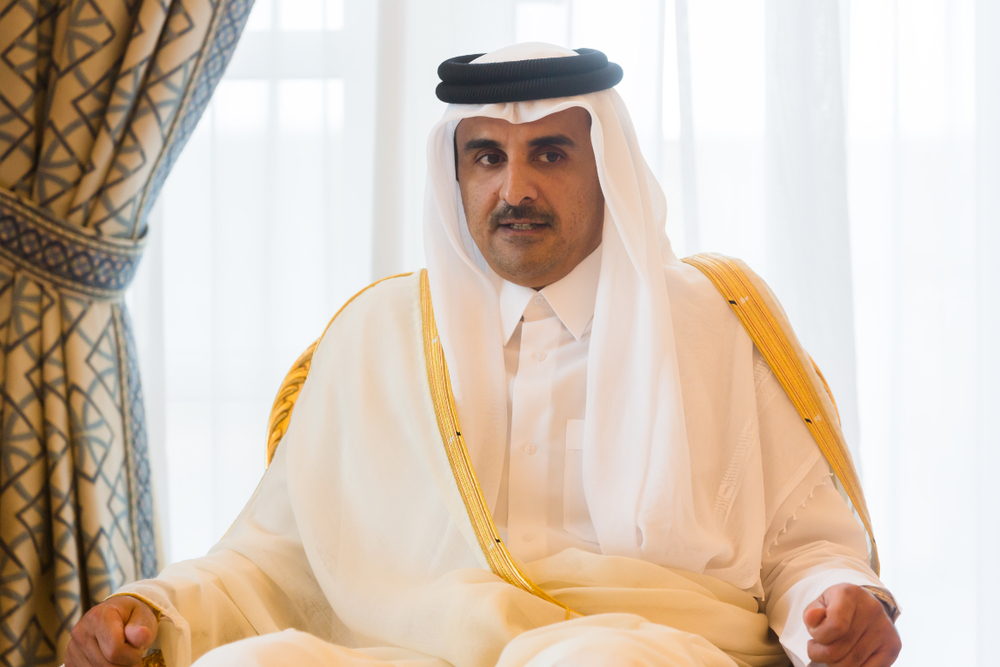

Qatar and absolute monarchy
The Emir of Qatar is currently Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani. He was appointed the eighth Emir of Qatar on June 25, 2013, following his father’s resignation.
In 2018, Tamim was the youngest reigning monarch of the GCC countries and the youngest sovereign in the world. He’s described as friendly and confident by those who have met him.
Tamim is closely connected to the Muslim Brotherhood and preserving the nation’s deep roots in Islamic traditions has been Tamim’s primary goal.
Qatar background and a short history
The Al Thani family has ruled Qatar since the mid-1800s. In the last 60 years, Qatar has transformed itself from a British protectorate known for pearling to an independent state with substantial natural gas and oil revenue.
The former Sultan, Amir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, overthrew his father’s rule in a peaceful revolution in the year 1995, bringing political reforms and unprecedented investments in the economy, and a rising Qatari leadership in the region.
This was achieved by establishing the pan-Arab satellite news network Al-Jazeera and Qatar’s mediation in several regional conflicts.
Saudi Arabia

Saudi Arabia and absolute monarchy
Saudi Arabia is a monarchy, with the reigning monarchy held by the House of Saud. The House of Saud has produced the majority of Saudi monarchs since its founding in 1744.
The kingdom was established by Muhammad bin Saud in 1744. The King of Saudi Arabia holds supreme power in the kingdom’s politics, and he is the leader of the House of Saud.
He also serves as head of government and head of state. He has executive as well as legislative and judicial power.
After ascending to the throne of the King, the King names his heir apparent, who will then become his Crown Prince. The Crown Prince is the first in the line of succession upon the passing of the King.
Everyone on the Council of Ministers is appointed by the King, who heads the Council by virtue of being the head of government. The most important appointments go only to the king’s immediate family.
Saudi Arabia background and a short history
Saudi Arabia is the birthplace of Islam and is home to the two most sacred shrines of Islam, in Mecca and Medina.
The current Saudi state was established on 19th December 1932 by Abd Al-Aziz bin Abd al-Rahman Al Saud (Ibn Saud), following a 30-year effort to unite the majority parts of the Arabian Peninsula.
The Holy Quran is the basis of Saudi Arabia’s constitution.
United Arab Emirates

The United Arab Emirates and absolute monarchy
The United Arab Emirates is a despotic monarchy despite having a federal system with a president and prime minister.
The UAE’s federal system comprises seven different monarchies comprising those of the Emirates of Dubai, Fujairah, Ajman, Umm al-Quwain, Abu Dhabi, and Ras al-Khaimah.
Despite seeming to be a constitutional, democratic nation, going by the information above, nothing could be further from the truth. The UAE has been called autocratic by many people.
The UAE is an autocracy that has the appearance of a modern contemporary state, but it is actually a tribal autocracy governed autocratically by the tribal rulers of each of the seven monarchies in the UAE’s federation.
Democratically elected institutions do not exist, nor does freedom of speech.
United Arab Emirates background and short history

In 19th century treaties, the UK gained control of the defense and foreign affairs of the Trucial States of the Persian Gulf. In 1971, six states, Abu Dhabi, Umm al Qaywayn, Dubayy, Ash Shariqah, Ajman, and Al Fujayrah, were merged into the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Later, in 1972, Ra’s al Khaymah joined the UAE.
The per capita GDP of the UAE is comparable to that of the wealthiest West European nations. The UAE has increasingly played an important role in regional issues in recent times.
Along with providing billions of dollars in economic aid to stabilize Egypt, the UAE was among the first nations to join the coalition to defeat ISIS.
On the 15th of September 2020, Bahrain and the UAE and Bahrain reached a peace deal (the Abraham Accords) with Israel.
The UAE and Bahrain were thus the fourth and third Middle Eastern countries, along with Egypt and Jordan, recognizing Israel.
Vatican City State

Vatican City State and absolute monarchy
Is the Pope a monarch? The answer is an unequivocal “Yes!” Popes have fought wars that have swept away territories as well as broken alliances; had a standing army, not to mention their personal bodyguards known under the title of the Swiss Guard, and strangled, suffocated, hanged, and poisoned adversaries.
They have had children out of wedlock, issued money, fought over succession; and generally did everything that kings do, and then some.
The Holy See is the jurisdiction of the Pope. Part of that jurisdiction is Vatican City State (the micronation’s official name).
However, the Holy See is larger than Vatican City State, as it includes the Diocese of Rome, the Latin Church, and the Catholic Church.
So, actually, the Pope is the absolute monarch of the Holy See, which is why he is the sovereign of the Vatican City, not the other way round.
Vatican City State background and short history
Popes in their secular capacity controlled parts of their respective regions of the Italian peninsula for over 1,000 years up to the middle of the 19th century, during which several in the Papal States were seized by the newly-unified kingdom of Italy.
From 1870 onwards, the papal spheres of influence were further restricted as Rome was annexed.
Around 1.3 billion people worldwide practice Catholicism, the largest Christian religion.