Although no exact number of sinkholes has been reported, Florida is the state with the most sinkhole-related damage.
Because sinkholes are a fairly common phenomenon in Florida, some residents experience difficulty finding a home safe from this occurrence. After all, even repaired sinkholes can cause problems.
Particularly sinkhole-prone counties in Florida include Pasco, Hernando, and Hillsborough, known together as “Sinkhole Alley.”
However, according to the Florida Geological Survey on the Florida Department of Environmental Protection (FDEP), no part of Florida is totally safe from sinkholes and their effects.
Table of Contents
How do sinkholes develop?
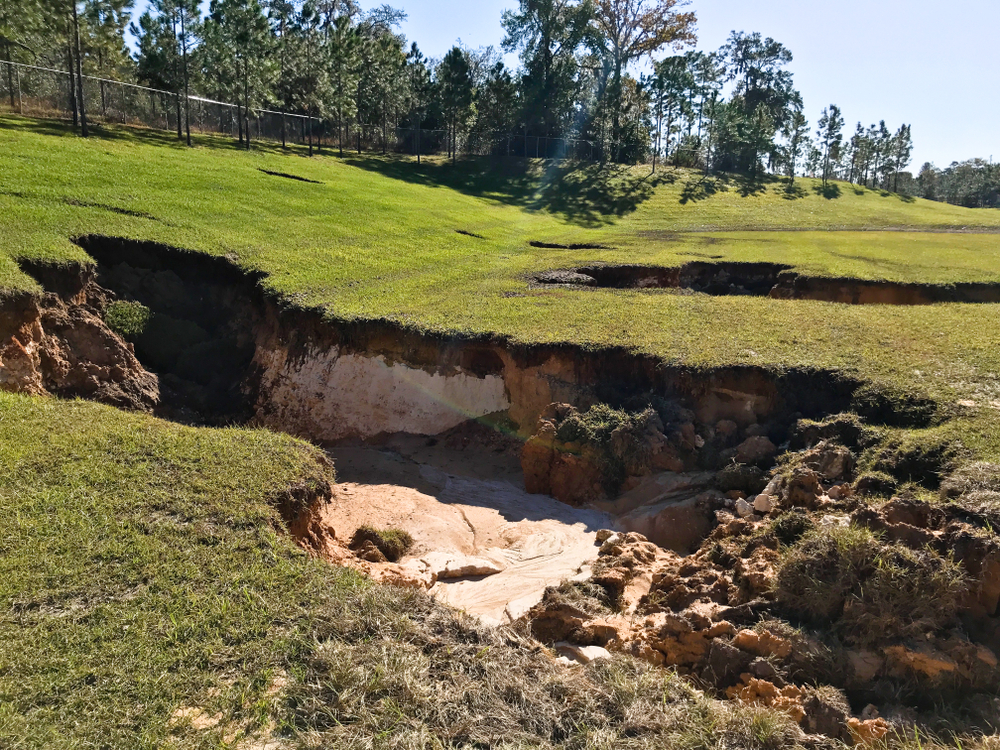

The Floridian peninsula is a porous plateau made up of a substantial amount of limestone, a hard sedimentary rock that’s especially susceptible to sinkholes.
The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) says that sinkholes are more likely to happen when the rock underlying the land surface consists of limestone, carbonate rock, salt beds, or other rocks that dissolve in the presence of groundwater.
When groundwater flows through spaces and cracks beneath the surface, limestone dissolves, resulting in a network of cavities and voids.
As the pores and cracks get bigger, the water gets more acidic, making the changes happen faster.
Sinkholes result when the land surface collapses into these cavities.
Droughts
Areas that experience drought, along with the groundwater withdrawals that follow the droughts, are at risk of having sinkholes. In addition, heavy rains that occur after droughts can make conditions favorable for sinkholes to develop.
Human Activities
The following human activities can increase the likelihood of sinkhole occurrences:
- High groundwater withdrawals
- Concentration of water in a certain area
- Human-made ponds and wells
Sinkhole Effects
Sinkholes are quite dangerous in urban and suburban areas because they can ruin highways and buildings.
Even when people manage to escape sinkholes unscathed, they still have to contend with the many expenses related to sinkhole damage.
Water quality troubles are also likely to develop. When a surface collapses, groundwater may end up in the aquifer, polluting many people’s major sources of drinking water.
What are the different types of sinkholes?
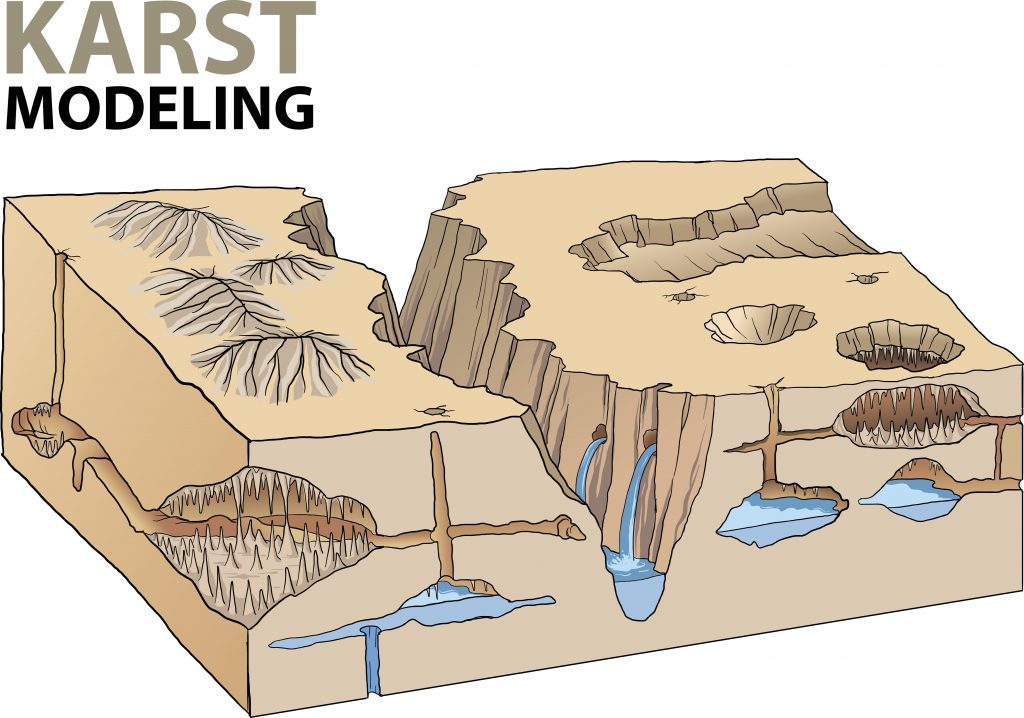
There are three main types of sinkholes. They are:
- Dissolution sinkholes – These sinkholes occur when there’s not enough ground cover, such as vegetation, on the bedrock. As a result of the lack of groundcover, water flows through the bedrock’s holes. A depression might develop in the ground, and the sinkhole might stop getting deeper if the bedrock is strong enough or if there’s enough ground cover blocking water flow. The result is a dissolution sinkhole in the form of a pond-like area or wetland.
- Cover-subsidence sinkholes – This type of sinkhole results from the permeability of the material covering the area, as well as the amount of sand it contains. As the sediment spills – or spalls, as geoscientists put it – into the bedrock’s empty caverns, a depression begins to form on the surface. The sediment buildup blocks the caverns, preventing water flow. However, these sinkholes never grow very large since the sediment prevents further erosion.
- Cover-collapse sinkholes – Cover-collapse sinkholes are the most dramatic and, perhaps, the most hazardous of all the types of sinkholes. This type of sinkhole occurs when the surface area, which is mostly made up of clay, spills into the cavities. Because clay is a strong material, arches develop. Over time, the arches hold up the surface ground until its layers become so thin that it collapses, bringing along with it everything that was on the surface.
Is it possible to predict sinkholes?
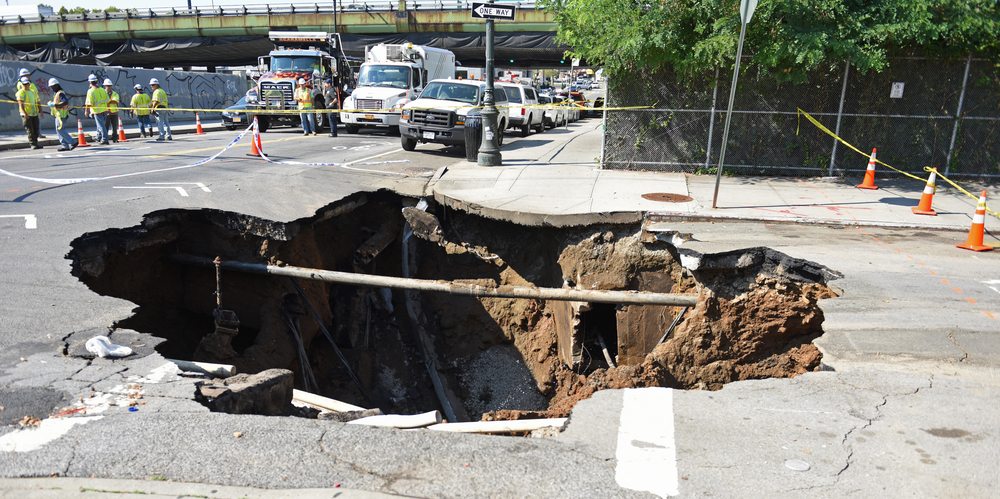

Although sinkholes are widely believed to occur suddenly, they actually take place over extended periods of time.
What this suggests is that there can be observable signs that a sinkhole is developing beneath the surface, signs that can end up saving people and their properties.
Signs to look out for below a building include cracks in walls and floors, polluted well water, and doors and windows that aren’t opening and closing properly.
One can also find signs in the ground as well, such as dying vegetation, buried items (e.g., fence posts, roots, foundations) coming out of the ground, the creation of new ponds, and slumping trees, fences, and other standing fixtures.
If a sinkhole does happen, the Southwest Florida Water Management District says that people should evacuate as soon as possible and inform their insurance agency and the city in which the sinkhole took place.
What other states have a lot of sinkholes?
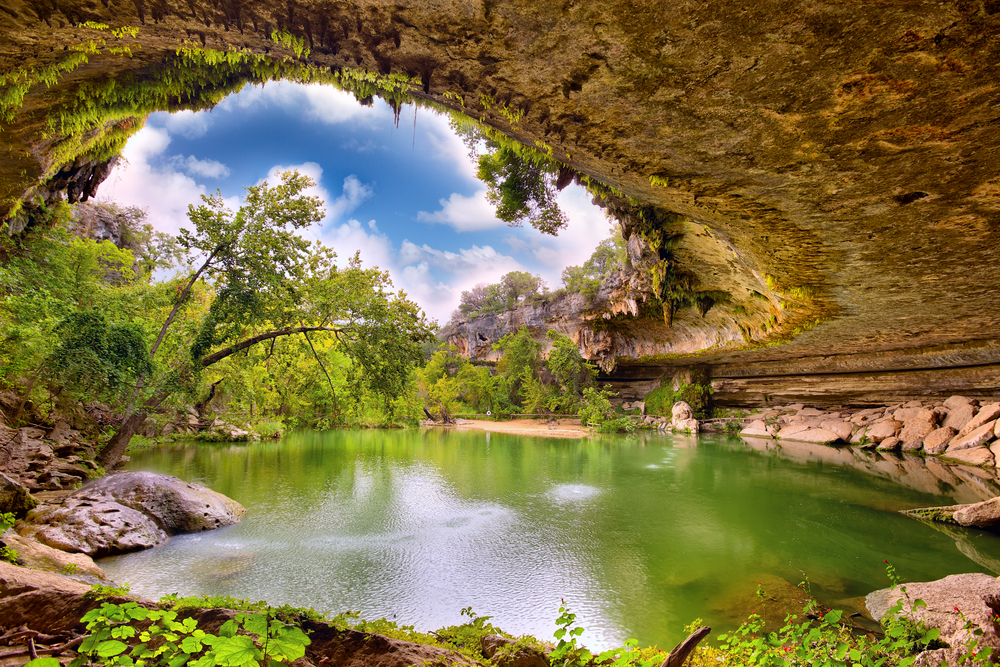

Due to their “karst terrain,” as geologists like to refer to them, Florida, Texas, Alabama, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, and Pennsylvania experience the most sinkhole damage.
In these states, the rock underneath the land surface (usually limestone or other easily dissolvable rock), naturally dissolves in the groundwater flowing through their cracks and crevices due to the type of material they’re made up of.
When rainwater travels through the soil, the rock ends up dissolving, creating spaces below the surface. When the cavities underground become too large, if the surface is too thin or there isn’t enough to support it, a sudden collapse may occur.
Due to the types of rock that make up a large portion of the South and parts of the Northeast, these incidents are quite common and have to be under constant watch.
Can sinkholes be prevented?
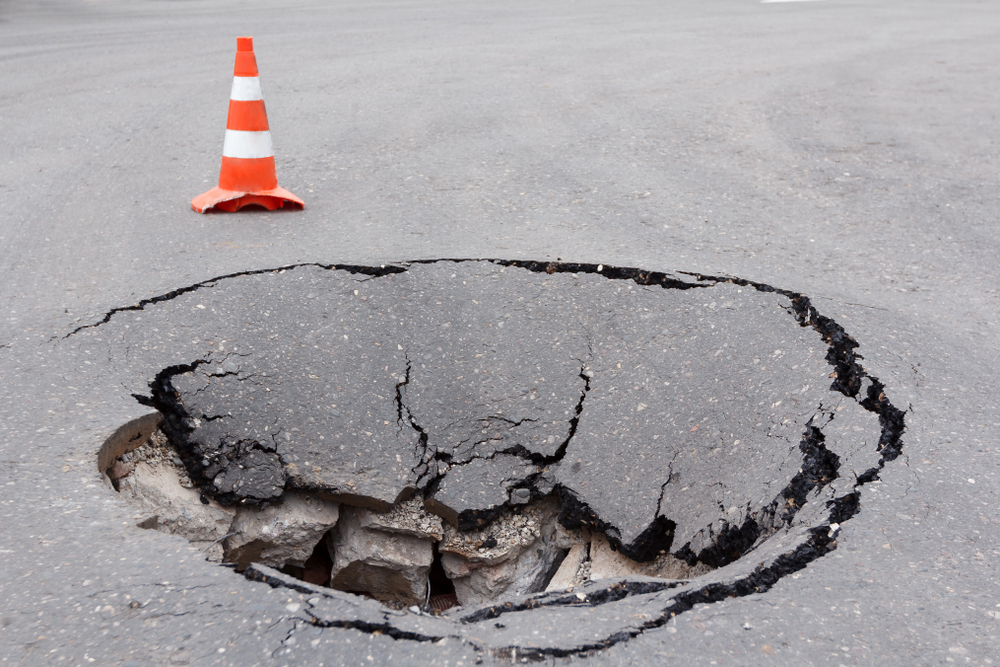

Many sinkholes are unpreventable. But sinkholes resulting from human activity can be prevented, especially ones that result from over-pumping groundwater.
In dry weather conditions, water flows through limestone or other dissolvable rock, which lies under the soil. Together, gravity, buoyancy loss, and pressure from the water can trigger a collapse, resulting in a sinkhole.
To prevent sinkholes caused by human activities, water tables must be maintained at a fairly high level. This can be achieved through water conservation rules and drought restrictions.
Examples include watering restrictions to prevent people from over-pumping water and reducing the water supply during times of drought.
It’s the district’s or state’s responsibility to ensure there’s enough long-term water supply for its people.
Water restrictions may feel like an inconvenience for some people and businesses, but they’re extremely important, especially during droughts.
People must also cooperate with each other to ensure the protection of the long-term water supply.
If district and state governments enforce rules for water supply and people follow those rules and cooperate with each other, their long-term water supply will be protected.
Thus, sinkhole occurrences will be reduced, and communities will be safer overall.