The field of zoology is fascinating and one that provides a multitude of interesting and educational information. It focuses on the animal kingdom both in the present and the past.
While zoology is one of the branches of biology, it has several individual sub-branches of its own.
The branches fall into two basic categories, specialization, which is determined by the animal type or species, and processes, which focus on animal functions.
A listing and information about what are considered the main branches of zoology sheds light on the purpose of the studies within each branch.
Since zoology covers a wide range of animals requiring research and study, there are numerous sub-branches dedicated to collecting information on diverse topics.
Table of Contents
Why is zoology important?

Zoology is a broad field of science that searches for the answers to many problems and questions that have yet to be answered.
It is an ongoing science dedicated to the animal kingdom and evolution.
Research and study play a vital and necessary role in many professional fields of work. Information gleaned from these studies has an impact on agriculture, dentistry, fisheries and poultry, medicine, veterinary science, and wildlife conservation, to name just a few.
Because humans depend upon the animal kingdom for products to support our lives, such as sources of food and pharmaceuticals, the different branches of zoology are not only important, but they are also necessary.
By conducting a series of ongoing studies within each branch on both living and non-living animals, zoologists can better understand a species’ life, habits, and behavior.
With this information, zoologists can also identify those animals that are endangered so they can be put on the endangered species list and be protected.
Does zoology have a focus?
Zoology does have a focus, which is studying the interaction of animals within their ecosystem.
This includes classification of the animal, its habits, embryology, how it has evolved through the centuries, and species that are now extinct.

When did the study of zoology begin?
Zoology has a long and ancient history with several key individuals contributing to the study of animals.
The ancient Greek philosopher, Aristotle, has been recognized as the father of zoology and biology.
He studied, investigated, and classified animals of his time (fourth century BC).
In the 12th century, the study and classification of the animal kingdom took a turn and began to be seen as a science focused on the anatomy and classification of animals.
In the mid-1500s, Conrad Gesner published his book, Historiae Animalium. Gesner wore many hats.
He was a doctor, professor, botanist, and naturalist. The encyclopedic-style book included an impressive amount of information about birds, fish, mammals, and reptiles.
The book contained five volumes and was considered the first writing covering natural history.
The volumes included four-footed beasts, egg-laying quadrupeds, birds, aquatic animals, and the last volume covered serpents.
On January 1, 1965, Thomas Boreman published his book, A Description of Three Hundred Animals; viz. Beasts, Birds, Fishes, Serpents, and Insects.
The book was a pictorial of the various zoological species.
What are the main branches of zoology?

- Biogeography
- Biology (developmental)
- Biology (evolutionary)
- Biology (molecular)
- Classification
- Ethology
- Invertebrate zoology
- Physiology
- Structural zoology
- Vertebrate zoology
A short description of what each of the main branches focuses on will help explain and clarify zoology and why it remains a necessary part of our ongoing life cycle on the planet.
What is biogeography?
This branch of zoology focuses on plants and animals and their geographic locations.
What is developmental biology?
As the name implies, developmental biology studies plant and animal growth and development.
What is evolutionary biology?
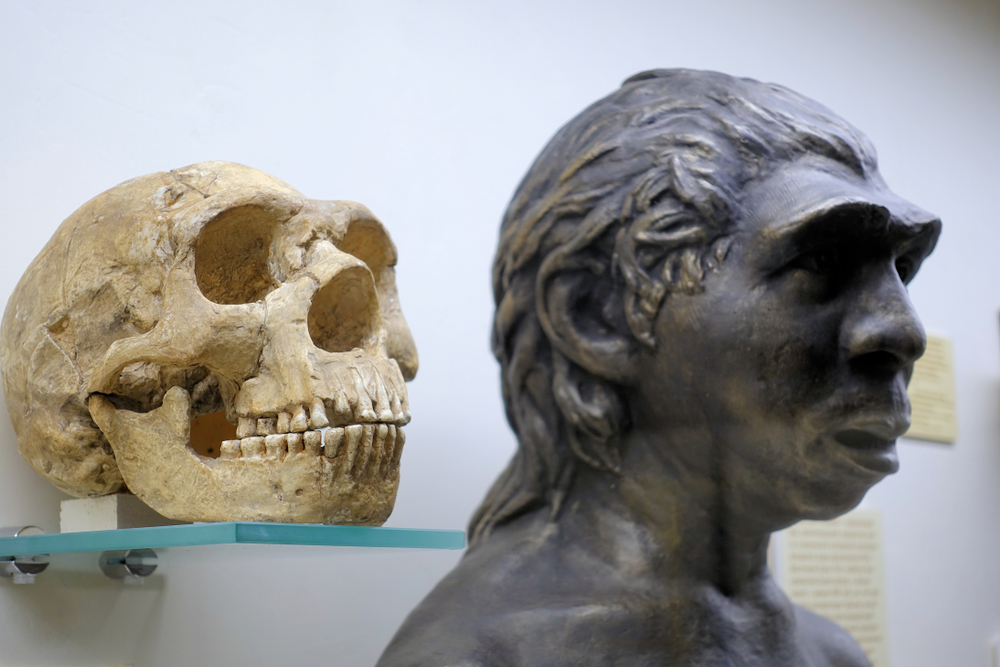

This field of study involves the evolutionary processes that resulted in the diverse plant and animal life on the planet.
Put simply, evolutionary biology studies the history of the many life forms, past and present, that inhabit or inhabited the Earth.
What is molecular biology?
The study of molecular biology gets down to the very basics of the structure and function of macromolecules that are essential for all living beings.
What does “classification” mean in Zoology?
When organisms are grouped by biological types, such as their species, the process is referred to in zoology as scientific classification.
What is the focus of ethology in zoology?
Ethology is a long-standing process dedicated to animal behavior that has remained constant throughout history.
This branch of zoology is a scientific process that studies animal behavior in natural habitats versus responses achieved in a controlled laboratory environment.
What does invertebrate zoology study?
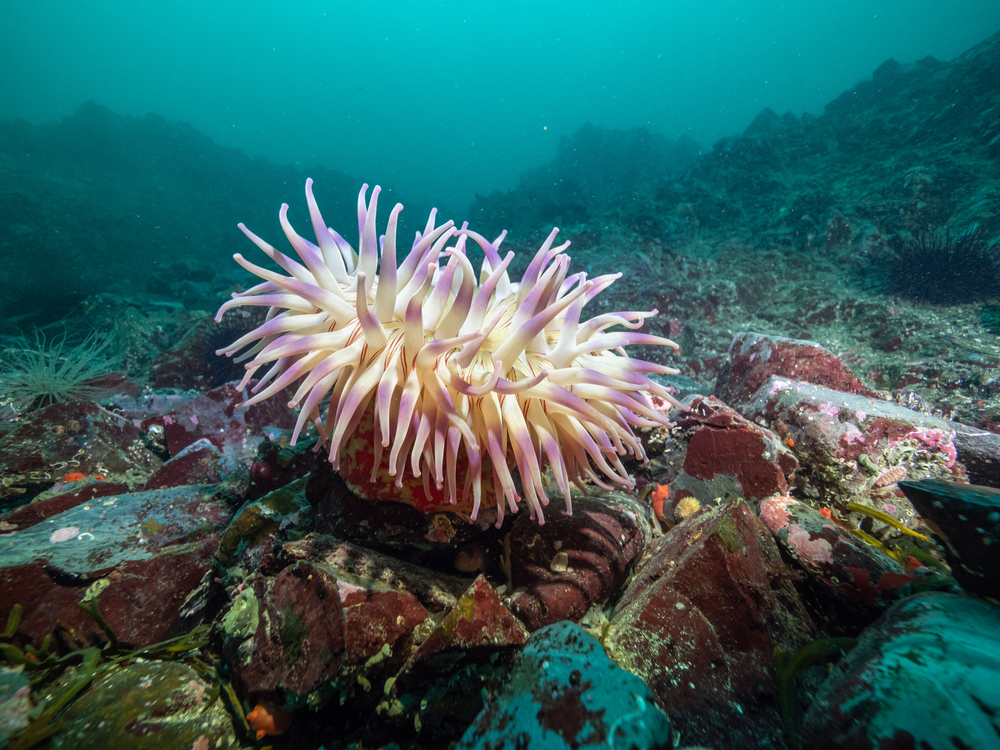

Researchers working in this branch of zoology are focused on studying animals without a backbone (invertebrates).
This group is diverse and makes up a significant population on the planet. Examples of invertebrates include earthworms, sponges, mollusks, amoebas, zooflagellates, leeches, sea urchins, squid, snails, spiders, assorted crustaceans, and more.
What is physiology?
Physiology is another interesting branch of zoology that meticulously studies organisms to determine their function in different environments.
Each part of an organism’s activity is analyzed to determine why that activity is chosen.
Is structural zoology important?
Structural zoology is important, as it takes the concept of research and study down to the very basics.
This branch is concerned with an animal’s cell biology at the molecular and microscopic levels.
In life, it is imperative to understand a cell’s structure and how it functions in all living organisms.
What is vertebrate zoology?
Vertebrate zoology is the opposite of invertebrate zoology. In this branch, animals with backbones are studied and scrutinized.
Generally, there are four divisions that make up vertebrate zoology. These are amphibians and reptiles (herpetology), ornithology (birds), fishes (ichthyology), and mammals (mammalogy).
Why are there so many branches of zoology?

The planet has a large and diverse population of animals that require study and research to understand the past and its impact on the living organisms of those times and to stay abreast of the functions and activities of animals that currently populate the planet.
Because of the numerous ways in which animals are studied (cellular, natural habitats, etc.), it is necessary and much more efficient to break down and divide the huge field of zoology into smaller branches.
Each branch is focused on a certain part of an animal’s makeup, anatomy, cell structure, and so forth.
By doing this, the information collected is clear, concise, and precise in that one area.
What are the sub-branches of zoology?
Along with the many main branches of zoology, there are also many sub-branches that further delve into the study, connection, and interaction that takes place within the animal kingdom.
These sub-branches include the following:
- Anatomy
- Anthrozoology
- Archaeozoology
- Arachnology
- Bionics
- Carcinology
- Cetology
- Cytology
- Ecology
- Embryology
- Entomology
- Ethology
- Evolution Environments
- Genetics
- Geology
- Herpetology
- Histology
- Ichthyology
- Mammalogy
- Malacology
- Morphology
- Nematology
- Neonatology
- Ornithology
- Paleontology
- Pathology
- Primatology
- Protozoology
- Taxonomy
- Zoography
- Zoogeography
- Zoometry
- Zootomy
Is the study of zoology popular?

Zoology and the study and research within its many branches covering the animal kingdom has remained a popular choice in the field of science.
For this reason, students who want to pursue a career in one of the main or sub-branches will find applicable courses and degree programs at many universities in the United States and in Europe.
Several of the top universities stateside offering animal and biology studies include the University of California-Davis, Cornell University, the University of Washington-Seattle Campus, University of California-Santa Barbara, North Carolina State University at Raleigh, University of Wisconsin-Madison, University of Vermont, Miami University, University of Florida, and Brigham Young University-Provo.
International destinations with established zoology courses and degrees include universities, such as the University of Cambridge (UK), Uppsala University (Sweden), University of Copenhagen (Denmark), Universidad Complutense de Madrid (Spain), University of Montpellier (France), University of Helsinki (Finland), University of Vienna (Austria), and the University of Glasgow (Scotland).

















