A plant cell is a type of cell that is found in plants. Plant cells are similar to other types of cells, but they have some unique features.
For example, plant cells have a cell wall, which helps the cell to keep its shape. Plant cells also have chloroplasts, which are organelles that help the cell to make food from sunlight.
Table of Contents
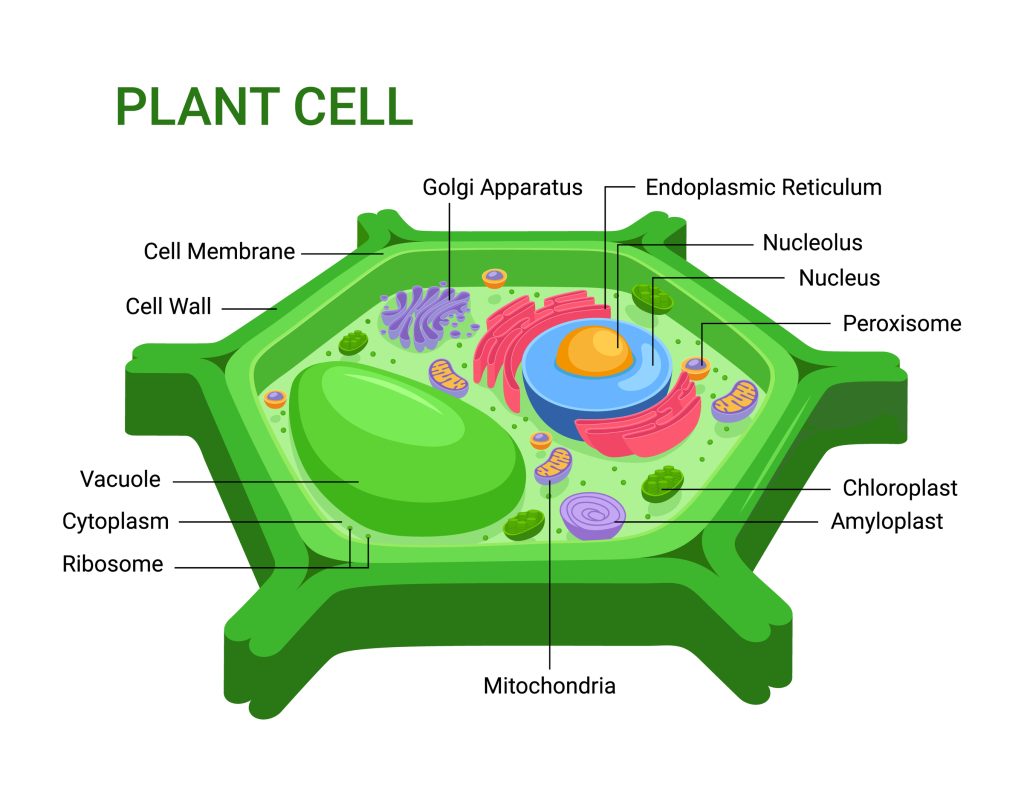
The Parts of a Plant Cell
The parts of a plant cell include the following:
1. Cell membrane
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and helps to protect it from the outside environment.
The cell membrane is made out of a lipid bilayer. This means that it is composed of two layers of fatty molecules called lipids.
The lipids are arranged so that their hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails are facing each other, and their hydrophilic (water-attracting) heads face outwards.
This arrangement creates a barrier that prevents water and other molecules from entering or leaving the cell.
2. Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, fibrous layer that surrounds the cell and helps to protect it from the outside environment.
The cell wall is made out of cellulose and other structural polysaccharides. These molecules are arranged in a network of fibers that gives the cell wall its strength.
3. Nucleus
The nucleus is a large organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material. This material is stored in the form of DNA molecules.
The nucleus also controls the cell’s metabolism and growth. The nucleus controls the cell’s metabolism and growth by regulating the activity of its genes.
It does this by producing proteins that control these processes.
The proteins produced by the nucleus include enzymes, hormones, and other molecules that regulate the cell’s metabolism and growth.
4. Chromosomes
Chromosomes are long strands of DNA that contain the cell’s genetic material. DNA is a molecule that contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism.
These instructions are stored in the form of genes.
Genes are segments of DNA that contain the instructions for making proteins. Proteins are molecules that play a variety of roles in the cell, including providing structure, performing biochemical reactions, and controlling gene expression.
5. Cellulose
Cellulose is a type of polysaccharide that makes up the cell wall. It is composed of long chains of glucose molecules.
It is the main component of the cell wall and gives it its strength.
6. Plastids
Plastids are organelles that play a role in photosynthesis. There are three types of plastids: chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts.
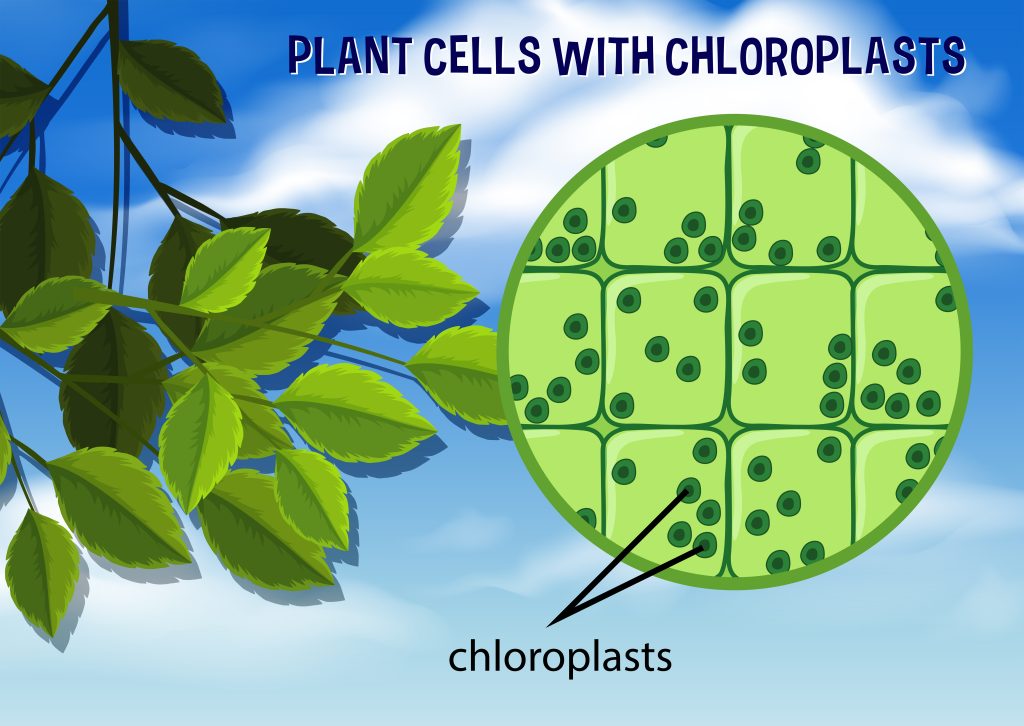
6. Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles that play a role in photosynthesis. They are green and contain the molecule chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy from the sun.
This energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Chromoplasts are organelles that play a role in the storage of pigments. They are usually red, orange, or yellow and contain the molecules carotenoids and flavonoids.
These molecules give plants their color.
7. Leucoplasts
Leucoplasts are organelles that play a role in the storage of nutrients. They are clear and do not contain pigments.
8. Vacuoles
Vacuoles are large, membrane-bound organelles that store water, enzymes, and other materials.
9. Lysosomes
Lysosomes are small, membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are made out of a variety of enzymes.
These enzymes help to break down molecules, such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
10. Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a series of interconnected tubes that run throughout the cell.
The endoplasmic reticulum is a system of membranes that helps to transport materials within the cell.
It is divided into two parts: the Rough ER and the Smooth ER.
The Rough ER gets its name from the fact that it is covered in ribs, or ribosomes. These ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins.
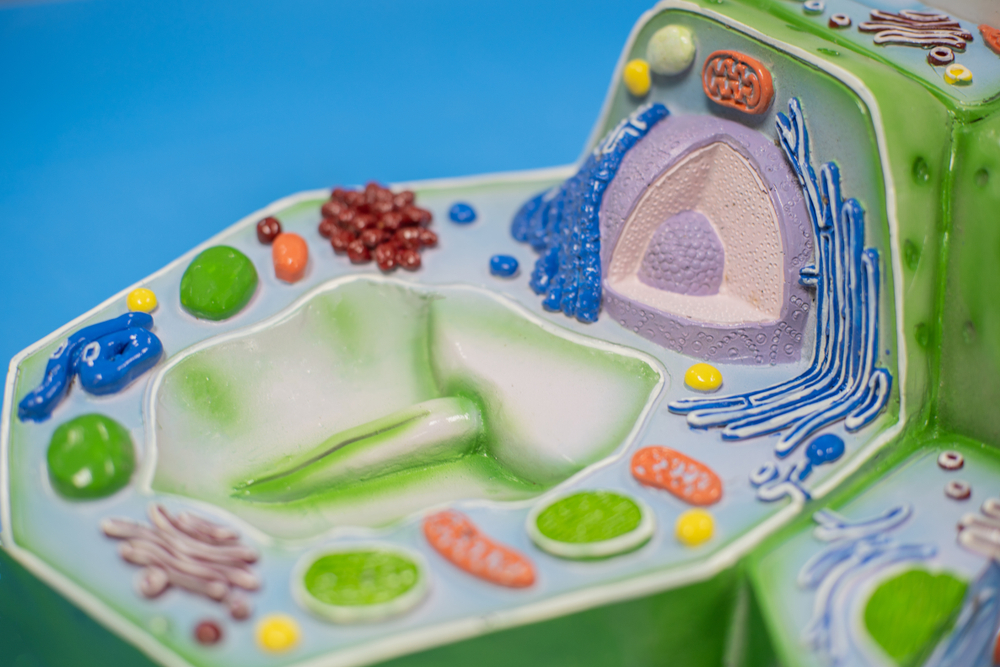
The Smooth ER does not have any ribs and is involved in lipid synthesis and drug detoxification.
11. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. They are made out of RNA and proteins1
13. Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle that helps to process and package molecules for export from the cell.
14. Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles that generate the majority of the cell’s ATP, or energy.
15. Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are small, membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes that remove toxins from the cell.
Peroxisomes are made out of proteins and lipids. They contain the enzyme hydrogen peroxide, which breaks down toxins into harmless molecules.
16. Cytoskeleton
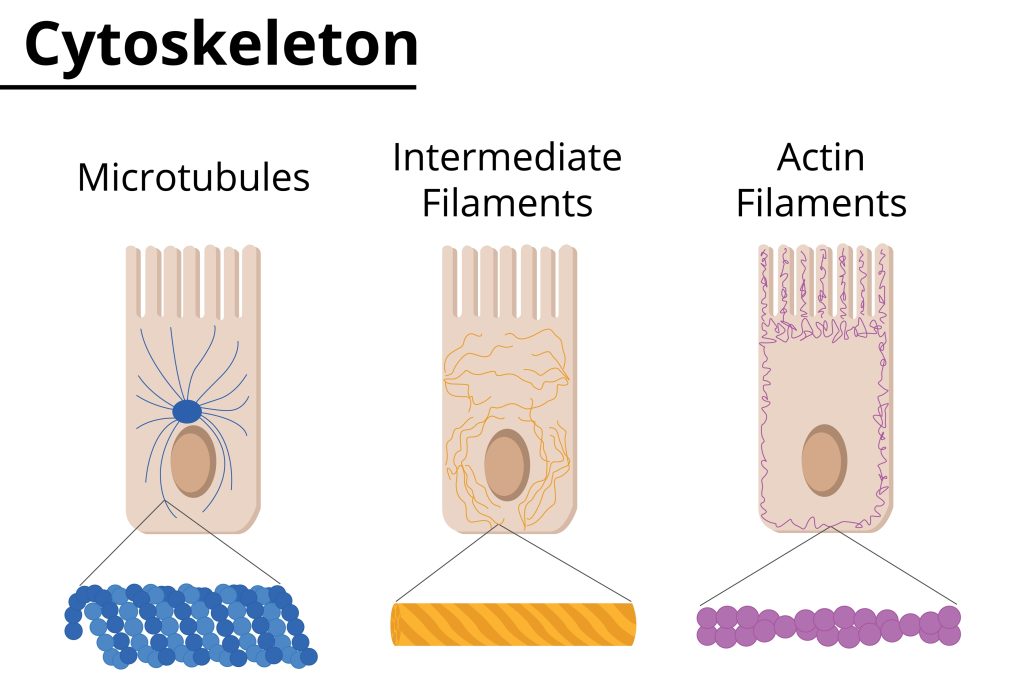
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibers that helps to maintain the shape of the cell. It also helps to transport molecules within the cell.
The cytoskeleton is composed of three types of proteins: microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments.
17. Microtubules
Microtubules are protein fibers that help to maintain the shape of the cell. They also play a role in cell division and transport.
18. Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments are protein fibers that help to maintain the shape of the cell. They play a role in cell division and stress response.
19. Microfilaments
Microfilaments are protein fibers that help to maintain the shape of the cell. They also play a role in cell movements, such as amoeboid movement and cytoplasmic streaming.
20. Lipids
Lipids are molecules that are insoluble in water. They include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids. Lipids play a role in cell membranes, energy storage, and hormone production.
21. Proteins
Proteins are molecules that are composed of amino acids. They play a role in cell structure, metabolism, and communication.
22. Microfilaments
Microfilaments are protein fibers that help to maintain the shape of the cell. They play a role in cell division and motility.
23. Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of proteins that gives the cell its shape and helps it to move.
The cytoskeleton is made out of a network of proteins, including actin and microtubules. These proteins give the cell its shape and help it to move.
The actin proteins are arranged in long filaments that can slide past each other, while the microtubules are stiffer and help to form the cell’s scaffolding.
24. Chromatin
Chromatin is the name for the genetic material (DNA) in the nucleus. This DNA is organized into chromosomes.
25. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for making proteins.
Ribosomes are made out of proteins and RNA. The proteins are responsible for assembling the RNA, and the RNA is responsible for carrying the genetic information to the ribosome.
This process is called translation.
26. Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubes that helps to process and package molecules for export from the cell.
Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a membrane-bound nucleus.
However, there are several important differences between the two types. For example, plant cells have a cell wall, while animal cells do not.
Plant cells also have chloroplasts, which are organelles that allow the cell to conduct photosynthesis.
Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Finally, plant cells tend to be larger than animal cells.
These differences between plant and animal cells are due to the different functions of these cell types.
Plant cells are primarily responsible for conducting photosynthesis, while animal cells are primarily responsible for respiration.
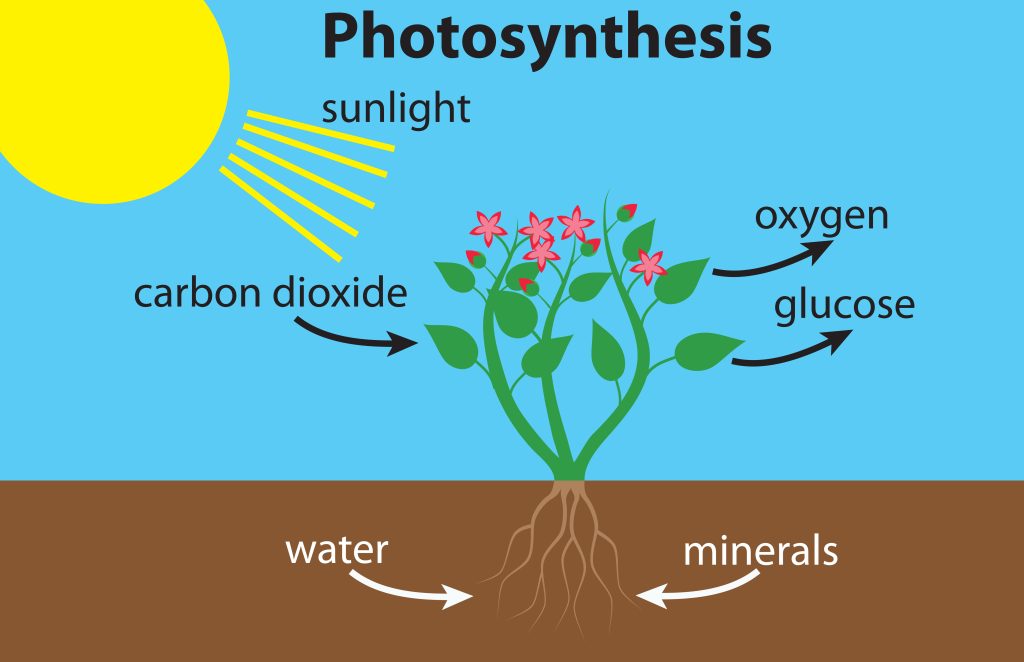
Because of their different primary functions, plant and animal cells have evolved to have different structures and organelles

















