When most people think of the human head, they think of the brain. However, that’s not the only organ that makes up the head.
Besides being home to the brain and the primary parts of the nervous system, the human head contains a number of important sensory organs, including the ears, eyes, mouth, and nose.
It’s also the start of the digestive system.
As you can see, the human head is home to some of the body’s most essential parts, which affect every aspect of people’s day-to-day lives.
Table of Contents
What are the main parts of the brain?
The three main parts of the brain are the cerebellum, the cerebrum, and the brain stem, and they each have their own functions.
- Cerebellum – The cerebellum, which is located at the back of the head below the cerebrum, is responsible for coordination and balance.
- Cerebrum – This part of the brain takes up most of the skull and controls problem solving, memory, emotions, and thinking.
- Brain stem – Located in front of the cerebellum and under the cerebrum, the brain stem connects the brain to the spinal cord. It’s responsible for functions such as breathing, heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure.
The brain is also separated into the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the occipital lobe.
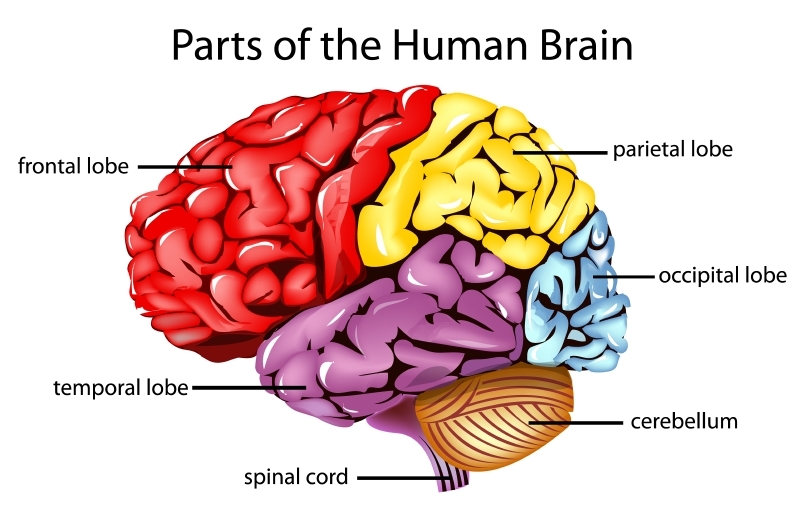
- Frontal lobe – The front part of the brain is known as the frontal lobe. This part of the brain is responsible for concentration, focus, self-control, planning, and managing higher-level executive functions.
- Parietal lobe – The parietal lobe is associated with sensation and the ability to feel, hear, and communicate through language.
- Temporal lobe – Located over the ears on both sides of the head, the temporal lobe is responsible for memory and also plays a role in language.
- Occipital lobe – Known for being primarily involved in visual processing, the occipital lobe is located in the very back part of the brain.
How much does a human brain weigh?
The average adult human brain weighs about three pounds and makes up about 2% of a person’s body weight.
Responsible for pumping blood to the entire body, the human heart pumps roughly 20% of its total output to the brain.
That means the brain receives about 20% of all the blood pumped through the heart, showing us just how important the brain really is.
The human brain is composed of around 100 billion neurons (i.e., brain cells) and is constantly changing.
Brain cells can die or regenerate over time due to a number of reasons. If someone, for example, has untreated chronic depression, they can lose brain cells.
The good news is that when depression is properly treated, the lost brain cells can regrow, allowing the brain to return to its original state.
What happens when the brain malfunctions?
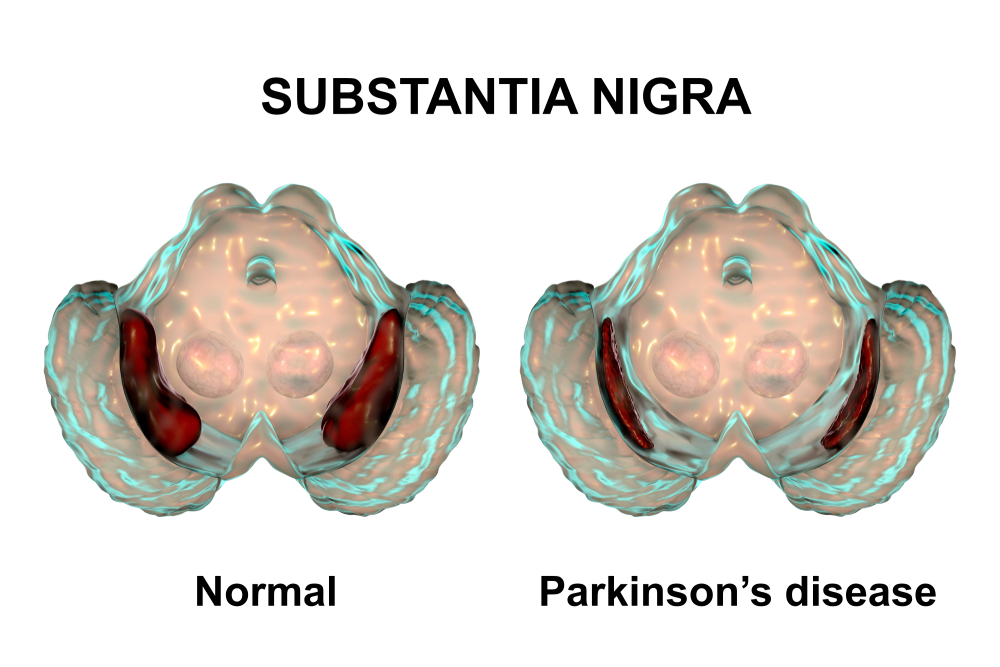
When chemicals in the brain malfunction, a variety of problems can occur. These include tremors, mental illnesses, symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, and a host of other issues.
In the human brain, there are electrical and chemical processes that give the brain the ability to interact and communicate with the nervous system.
Neurotransmitters send messages between neurons that pass information through electrical signals.
With the malfunctioning of the chemical processes of neurotransmitters comes mental illnesses like anxiety and depression.
When the electrical signals fail to function properly, issues like tremors, Parkinson’s disease symptoms, seizures, and other motor system disorders can result.
Does the brain go to sleep when we do?
Contrary to popular belief, the brain is very active when we’re asleep. The primary difference between being asleep and being awake has to do with which brain systems are being activated at a given moment.
Neurotransmitters, which are chemicals in the brain, act on different nerve cells (also known as neurons) within the brain, dictating which parts of the brain will be activated while we’re sleeping and telling the brain to fall asleep.
Sleep is also important for brain functions while we’re awake, including concentration, memory, creativity, coordination, and wellbeing.
It’s essential to get adequate sleep so you can strengthen and repair these areas. Without enough sleep, people often find it difficult to function.
What percentage of your brain do you use?
Although it’s widely believed that you use only 10% or less of your brain, the fact is that you use 100% of your brain, just not all at the same time.
The brain makes up about 2% of your total body weight.
However, it uses up about 20% of your energy, indicating that there’s a significant amount of activity in the brain.
Even the smallest activities consume more than 10% of your brain, and how much is consumed depends on what you’re doing.
Does damage to one side of the brain affect the other side of the body?
Your brain is divided in the middle and comprises two sides, also known as hemispheres. Each hemisphere controls the muscles on the opposite side of the body.
For example, the left hemisphere controls the muscles on the right side, and vice versa.
If one side of the brain gets damaged due to a stroke or traumatic brain injury (TBI), the opposite side of the body will be impacted.
While your left brain hemisphere is responsible for your math, language, and logic skill development, your right brain hemisphere is in charge of your facial recognition, spatial and musical abilities, and visual imagery.
Is short-term memory lapse a sign of brain decline?
Short-term memory loss does tend to correlate with age, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that Alzheimer’s disease or dementia is developing.
As we age, it’s common to forget things like people’s names and where you put your car keys.
It can be very concerning when this happens, but memory lapses aren’t always indicative of severe mental decline.
As a matter of fact, the majority of older adults don’t develop Alzheimer’s disease. Less than 20% of people 65 years old and above will be diagnosed with the condition.
If you’re experiencing memory loss and are concerned, you should talk to your doctor.
What chemical in the brain is associated with pleasure?
The neurotransmitter in the brain that’s associated with pleasure is dopamine.
This chemical is also responsible for body movement and functions like attention and motivation.
With decreases in dopamine activity comes the development of disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia.
Certain medications that are used to treat such disorders work by altering dopamine levels in the brain.
Serotonin is another widely known neurotransmitter. In addition to helping you sleep, this chemical influences mood, behavior, pain perception, appetite, and body temperature regulation.
Drugs that are given to increase levels of serotonin are often used for treating depression, obsessive-compulsive disorders (OCD), and eating disorders.
Lastly, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a neurotransmitter in the brain that affects muscle activity.
To treat disorders like Huntington’s disease and epileptic seizures, doctors prescribe drugs that increase GABA levels in the brain.
Does the skin of the head differ from the skin of other areas of the body?
Yes, the skin of the head tends to be thinner and more sensitive than the skin in other parts of the body.

This is especially true for the skin around the eyes. Because the skin around the eyes is thinner than the skin in other areas of the body and lacks the fat that cushions the skin, it’s more susceptible to skin conditions and irritants.
As a result, it’s important to moisturize regularly, avoid harsh skincare products, and drink plenty of water.

















