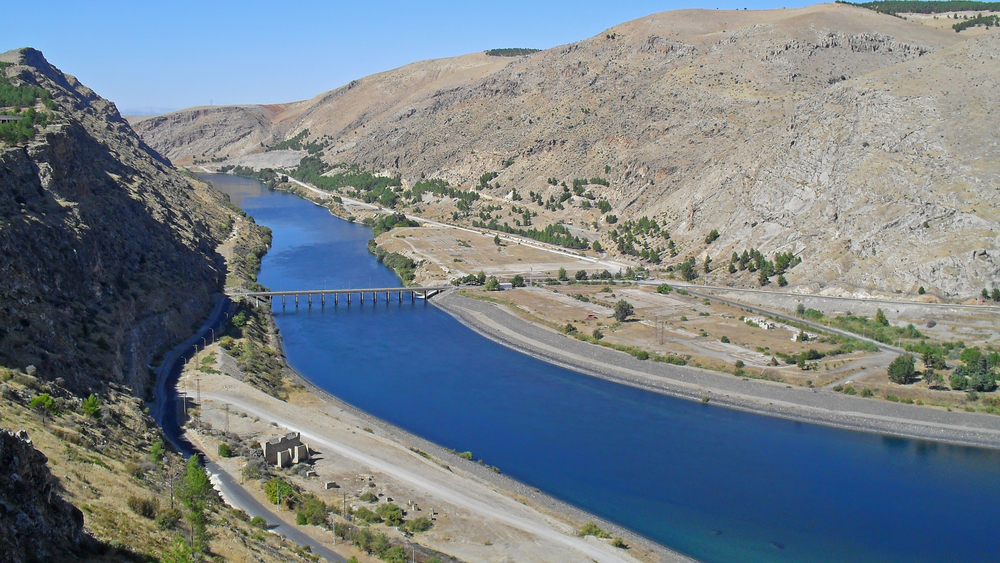
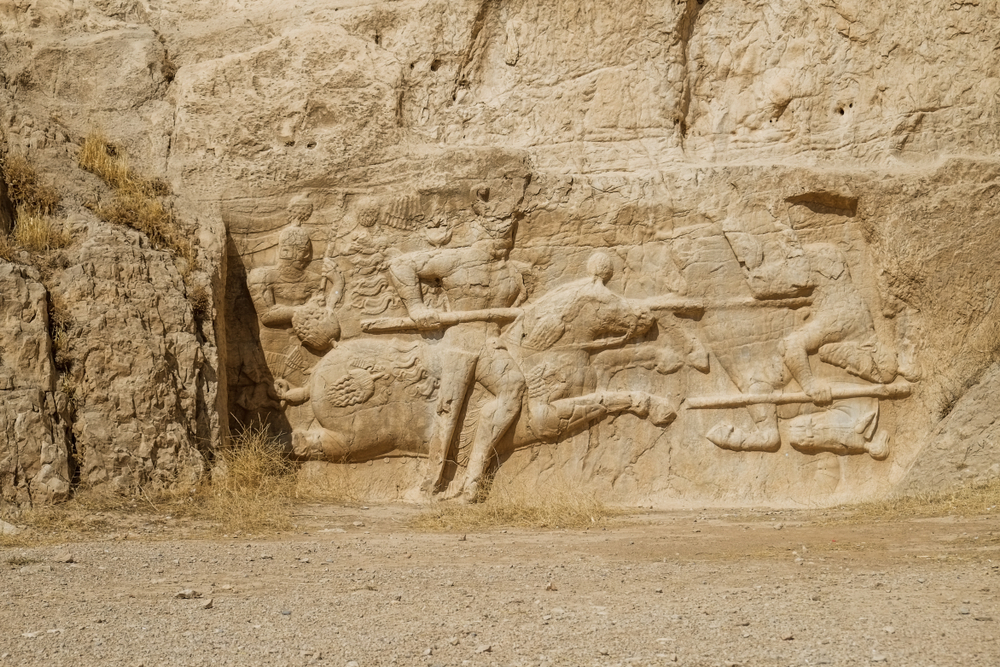
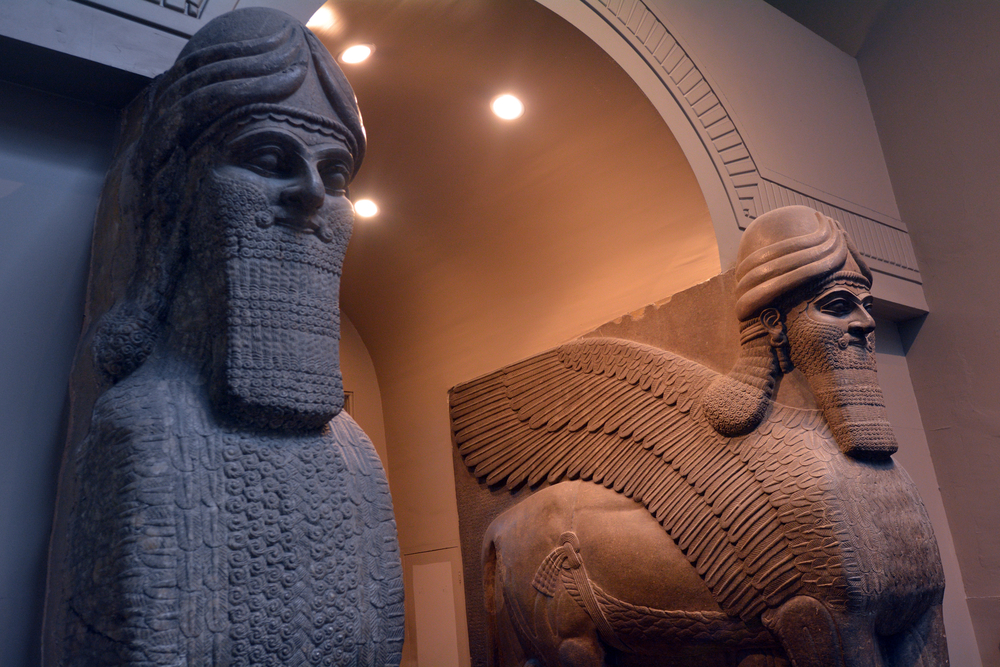
The ancient Greek term for the land between two rivers is “Mesopotamia”.
These two rivers emerge from eastern Turkey and continue flowing south, heading towards the Persian Gulf.
The names of these two estuaries are the Tigris and the Euphrates rivers.
Another name for Mesopotamia is the great semicircle or the Fertile Crescent. It is called this because of the way it stretches from east to west in the form of a giant arc.
The mountains look down on the shores of this desert bay. It is not a bay filled with water, but with around eight hundred kilometers astride sandy waste.
This bay is formed as an extension of the northern Arabian desert that sweeps the northeast section of the Mediterranean’s latitude.
Table of Contents
What is the Fertile Crescent Region?
This is a region of the Middle East that is shaped like a boomerang. The Fertile Crescent, also referred to as the “Cradle of Civilization,” was the domain to ancient human developments.
The Crescent Region is also where various innovations of technology were born, such as the wheel, writing, irrigation use, and agriculture.
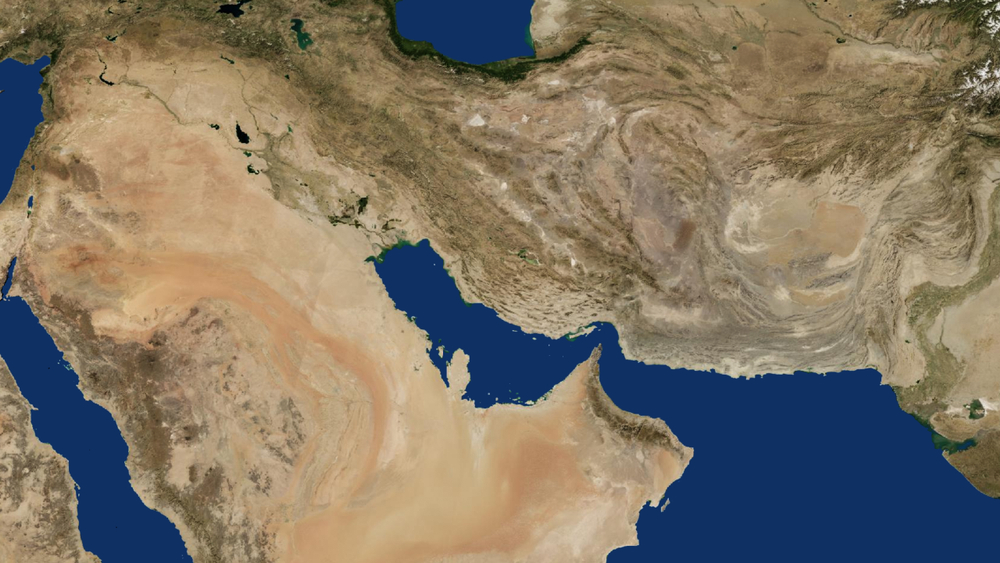
The name “Crescent Region” derives from how it stretches out in the shape of an arc. Going west from the Mediterranean Sea to the eastern region of the Persian Gulf, this entire area has excellent agricultural uses.
The region known as the Fertile Crescent includes the following countries:
- Egypt
- Jordan
- Lebanon
- Iraq
- Israel
- Palestine
- Syria
This is in addition to the areas that surround Iran and Turkey along with the Euphrates and Tigris rivers. It also includes sources of river water provided by the Jordan River.
To the south is the arid atmosphere the Syrian Desert provides along the boundary inside and toward the south. The Anatolian highlands are found on the outside boundary of the Crescent.
You will also notice highlands located in the north. To the west are the Sahara Desert, the Iranian Plateau to the east, and Sudan in the south.
Is the Fertile Crescent a desert?
The Fertile Crescent is the ground lying amidst the Euphrates and Tigris rivers. Baghdad is south of this region, and it is designated as a silt desert.
The soil is arid, yet fertile, due to the many deposits provided by the rivers over several million years.

The first civilization in this region were the Sumerians around 3,500 B.C. During this era, the region received a little more rainfall, but not by much.
What Is the Fertile Crescent famous for?
The Fertile Crescent received its moniker because of the opulent ground that was utilized for the use of irrigation and agriculture.
Its soil was so fertile because the two nearby rivers were continuously dumping silt into the land. The routes for trading and farming were made accessible by way of these two rivers.
Those that wandered the desert grasslands and the north’s mountain people held an age-long struggle throughout Western Asian history.
Currently, there is still an ongoing struggle over who will possess the shores of this desert bay and the Fertile Crescent.
What challenges has the Fertile Crescent faced?
The waters that flowed from the Fertile Crescent area were what made Iraq, Syria, and Turkey. The rivers are beginning to deplete the soil that was once fertile because of an advancing population and urbanization.
Several dams have also been built, which have affected the quality and decreased water output.
How is the Fertile Crescent a strain on the environment?
Syria’s continued conflict is only one reason for tensions in the region. The other was because an area that was once thriving and lush was now a strain on the environment.
The early 2000s brought geographic as well as political issues to the Fertile Crescent. These conflicts became entangled as people fought for control of the region.
A series of large-scale projects were also created during the 1950s to divert the water away from the Mesopotamian marshes.
This diversion resulted in the drying up of the river system known as the Tigris-Euphrates. Therefore, the Fertile Crescent is not as fertile as it once was.
Who or what destroyed the Fertile Crescent?
The Fertile Crescent region was conquered by the Sassanid Persians following an annexation by the Romans that was short-lived. Following this, during the 7th century, the Arabian Muslims took over the region.
This area is now referred to as Syria, Jordan, southern Iraq, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, sections of Turkey, Iran, and Egypt. It earned the moniker Fertile Crescent because of the abundant water sources this region provided to earlier populations.
Ancient populations became entrenched in the Fertile Crescent because it contained an abundance of water. The Arab leaders were able to maintain the Fertile Crescent system until the 1200s.
After experiencing several partially failed attempts, the system eventually collapsed.
Which countries are currently part of the Fertile Crescent?
Currently, the geographic area that is the Fertile Crescent contains the following modern-day countries:
- Iran
- Iraq
- Syria
- Israel
- Jordan
- Turkey
The north-eastern section of Egypt is another part of the Fertile Crescent. This area is supported by several civilizations of ancient descent and is fed by the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Why is the Fertile Crescent civilization declining?
The erosion of the Fertile Crescent civilizations has been progressively declining since the last Ice Age.
It has been 8,000 years since the neighbors of Iraq embodied the term “civilization” that led the world.
Power, ideas, and technology continued to flow away from Iraq and towards Europe, eventually arriving in America. The world should take heed and pay attention to the decline of Iraq.
The Mediterranean atmosphere was once a place they were lucky enough to live and produce plants and domesticate the animals.
The people who lived here until around 8500 BC hunted animals and collected plant life for sustenance. Herding and farming became a way of life for the Fertile Crescent and Iraqi people.
They harvested wild peas, barley, and wheat, while also domesticating the pigs, sheep, cows, and goats. Currently, these crops and livestock remain to be one of the world’s staple products.
The explosive population that was energized by agriculture also created the need for full-time specialists. These specialists were needed to generate a surplus of food for the population.
They were not required to spend their time producing food for themselves.
Who were these specialists?
Metalworkers and smiths were the specialists that this budding agriculture needed. These specialists were the ones to create some of the first copper equipment used worldwide back in 5000 BC.
In 3000 BC, they created the first tools made of bronze, and in 1500 BC, made tools of iron.
Some of these specialists were also scribes and accountants, and these were the people responsible for the creation of the world’s primary system of writing about 3400 BC.
Writing didn’t completely get to where it is known today in the United States until some 5,000 years afterward. All of these facts make the rate of illiteracy in Iraq an irony that is particularly cruel.
What civilizations were part of the Mesopotamian Empires?
There were six different Mesopotamian Empires that lived within the Fertile Crescent. Some famous ones include the Akkadian, Babylonian, and Neo-Babylonian Empires.
What was the Akkadian Empire?
Following the civilization of Sumer, which was long-lived, came the first empire of Mesopotamia – the Akkadian Empire. The empire was centralized in the city of Akkad and the regions surrounding it.
The Akkadian Empire brought together the Sumerian and Akkadian speakers to work under one government.
The Babylonian Empire
In 1894 B.C., the small town of Babylon emerged, originating as a small Amorite-governed state.
Babylonia was founded in the central-southern portion of Mesopotamia – what we know as Syria and Iraq today. The ancient Akkadian-speaking state of Babylonia was just a small town during the Akkadian Empire.
During the Hammurabi reign in the 18th century, it quickly evolved into the capital city it is known as. The country of Akkad is how Babylonia was often referred to by many during the Akkadian Empire.
Babylonia was often the rival of Assyria and Elam. Assyria is to the north and Elam is east of the Ancient city of Iran. For a short time, Babylonia was the primary power of this region following the Hammurabi reign.
When Hammurabi died, the Babylonian Empire quickly fell apart and transformed into a smaller kingdom.
The clay tablets–dating back to the 23rd century BC– are the earliest mention of Babylon city. These clay tablets originated during the Sargon of Akkad’s reign (2334 -2279 BC).
Primarily a cultural and religious hub, Babylon was neither a large city nor an independent state. It was subject to the Akkadian Empire, just as the rest of Mesopotamia was.
This united the Sumerian and Akkadian speakers.
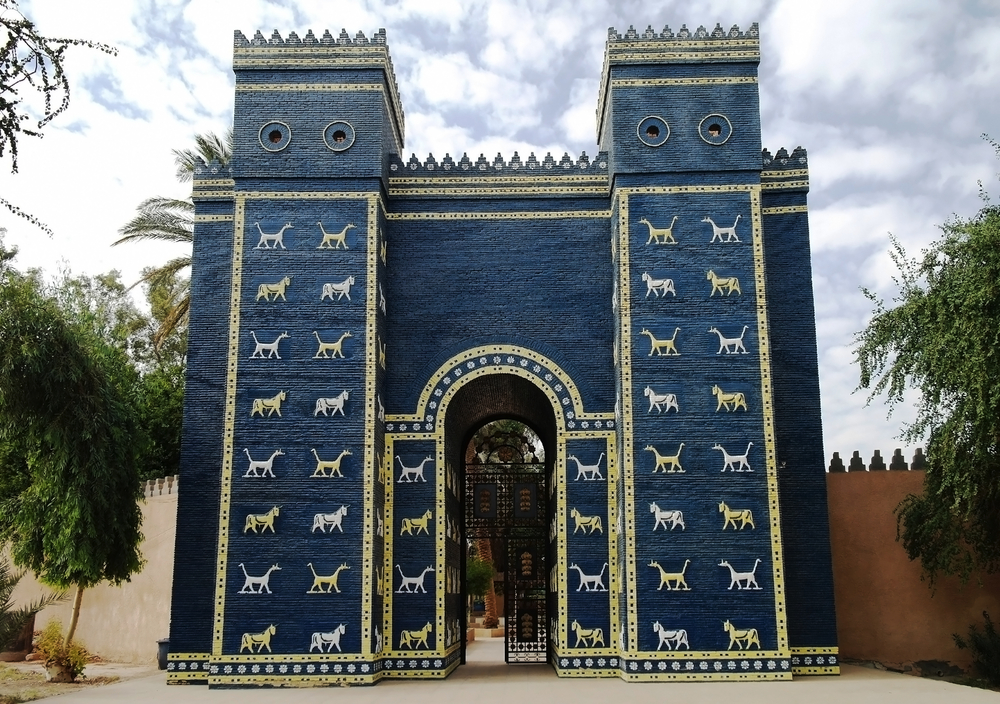
The Neo-Babylonian Empire
This was the Second Babylonian Empire, called the Neo-Babylonian Empire. It was also referred to as the Chaldean Empire, historically.
These were the remaining empires of the Mesopotamian people, led by the native monarchs of Mesopotamia.
The architecture they produced was what the Neo-Babylonians were popular for. Particularly that of the capital city of Babylon.
This city was called Nebuchadnezzar and was an ancient city that included seven gates and walls. It is often referred to by Roman and ancient Greek writers as the legendary “Hanging Gardens.”
Who was the ruler of the Neo-Babylonian Empire?
For three centuries, the Akkadians and Assyrians ruled Babylonia. However, following the death of the last Assyrian ruler, the external yoke was discarded.
It was under King Nebuchadnezzar II that Neo-Babylonian architecture and art would peak. This king ruled during the period of 604–562 BC.
What became of the Neo-Babylonian Empire?
This empire lasted only a little over two decades – 23 years after it formed it came to an end in 539 BC. This was the time during which Cyrus the Great led his troops to overcome the city of Babylon.
This area would later become a section of the Persian Empire which eventually succumbed to Alexander the Great. Currently, the region we call Iraq is actually the ruins of Babylon.
Final thoughts
The early settlers chose to live in Mesopotamia because it was near two extremely large bodies of fresh drinking water. This water would also provide a means to grow produce and raise livestock.
Mesopotamia meant a way of survival for the early settlers.
For the traveler, it is a place to learn about the ancient ruins of the Babylonian civilization. If you are a history buff, then visiting this ancient land will be a worthwhile trip.
It is a smaller destination for tourists but coming to Mesopotamia is enlightening. There are so many unique things to see and do in this hidden destination.